The Basics of Investing in the Foreign Exchange Market & Carry Trade
The foreign exchange (Forex) market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with average daily trading volumes exceeding 5 trillion US dollars. This expansive market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, across major financial hubs including London, New York, Tokyo, and Sydney, facilitating currency trading among governments, central banks, corporations, financial institutions, and individual traders.
Forex is an over-the-counter (OTC) market where transactions are conducted electronically between participants. Its vast liquidity stems from its global scope, as currencies are continually in demand for international trade, investment, and hedging against economic risks.
Due to its high liquidity and accessibility, Forex attracts a broad spectrum of participants—from multinational corporations managing foreign exchange risk to retail traders aiming to profit from short-term price movements. However, the market’s volatility and use of leverage also introduce significant risks, making informed strategies and sound risk management essential for success.
Most Influential Players in The Foreign Exchange Market

The most influential participants in the Forex market are central banks, commercial banks, and institutional investors. Together, banks and institutional investors account for approximately 50% of daily turnover. Exporters, importers, and other multinational corporations contribute around 10% of daily turnover.
Central Banks
Central banks play a crucial role in the currency market. They possess both the tools and the incentives to influence domestic exchange rates as part of their monetary policy implementation—particularly the U.S. Federal Reserve (FED), the European Central Bank (ECB), the Bank of Japan (BoJ), the Bank of England (BoE), and the Swiss National Bank (SNB). One should never trade against these five central banks.
Arsenal of Central Banks
Central banks possess a wide array of tools to intervene in the foreign exchange market. However, when it comes to implementing monetary policy, they primarily rely on four major tools:
-
Adjusting the Basic Interest Rate
By changing the basic interest rate, central banks can influence inflation, unemployment, consumption, investment, and overall economic growth.
-
Adjusting the Discount Rate
The discount rate is the interest rate central banks charge when lending to commercial banks. Its level directly impacts market liquidity.
-
Open Market Operations
Central banks can buy or sell securities at any time. When a central bank purchases securities from a commercial bank, it injects cash into that bank’s reserves, thereby increasing overall market liquidity. These activities, known as open market operations, are key tools for executing monetary policy.
-
Reserve Requirement
The reserve requirement is the amount of funds that commercial banks are required to hold overnight. Lowering this requirement increases the amount of money banks can lend, thus boosting liquidity.
Fixed vs. Flexible Exchange-Rate Systems
The choice between a flexible or fixed exchange-rate system lies with each country’s monetary authorities. Most Western economies operate under flexible exchange-rate systems.
(a) Flexible Exchange-Rate System
A flexible exchange-rate system allows the domestic currency’s value to be determined by market forces of supply and demand. An increasing number of countries are adopting this system, often viewed as a sign of economic liberalization for foreign investors.
(b) Fixed Exchange-Rate System
A fixed (or pegged) exchange-rate system ties the domestic currency’s value to:
-
Another currency (e.g., the Euro or the U.S. dollar)
-
The value of gold
-
A basket of other currencies
Foreign Exchange Reserves
All major economies maintain foreign exchange reserves. These reserves consist of assets held in one or more reserve currencies—primarily the U.S. dollar, Euro, Japanese yen, Swiss franc, or British pound sterling. Gold reserves are also included in the total foreign exchange reserves.
-
The U.S. dollar accounts for approximately 64% of all known central bank foreign exchange reserves.
-
The Euro accounts for about 20%.
Monetary authorities use these reserves to stabilize their domestic currencies during times of financial stress and to deter speculative attacks that might cause undesirable currency volatility.
Table: Countries with the Largest Forex Reserves
|
A/A |
Country |
Foreign Currency Reserves (in millions USD) |
|
1 |
China |
$3,200,000 |
|
2 |
Japan |
$1,250,000 |
|
3 |
Switzerland |
$800,000 |
|
4 |
Saudi Arabia |
$500,000 |
|
5 |
Russia |
$460,000 |
|
6 |
Taiwan |
$460,000 |
|
7 |
Hong Kong |
$425,000 |
|
8 |
India |
$405,000 |
|
9 |
South Korea |
$400,00 |
|
10 |
Brazil |
$380,00 |
Source: IMF (2018), Investopedia
Forex Pairs Trend Well
Trading with the trend is arguably the smartest strategy in the foreign exchange market. Professional traders often say, “The trend is your friend.” Long-term traders can combine the Carry Trade Strategy with the Trend Trading Strategy to maximize profit potential.
Defining the Trend:
-
An uptrend occurs when the market consistently forms higher highs and higher lows (on the weekly chart).
-
A downtrend occurs when the market consistently forms lower highs and lower lows (on the weekly chart).
-
Alternatively, if the market is trading above its 200-period moving average, it is generally considered bullish; if below, it is generally considered bearish (on the daily chart).
Revealing Key Seasonal Forex Patterns
Seasonality plays a significant role in financial markets—especially in the foreign exchange market. Due to the structure of the global monetary system, currencies often follow seasonal patterns. The dynamics of supply and demand shift over time, and certain months of the year tend to bring about specific trends.
Example: The British Pound Sterling
-
Traditionally bearish in February
-
Strongly bullish in April (16 out of 19 bullish periods between 2000–2018)
-
Bearish in August
Chart: GBP vs. USD – Seasonality 2000–2018
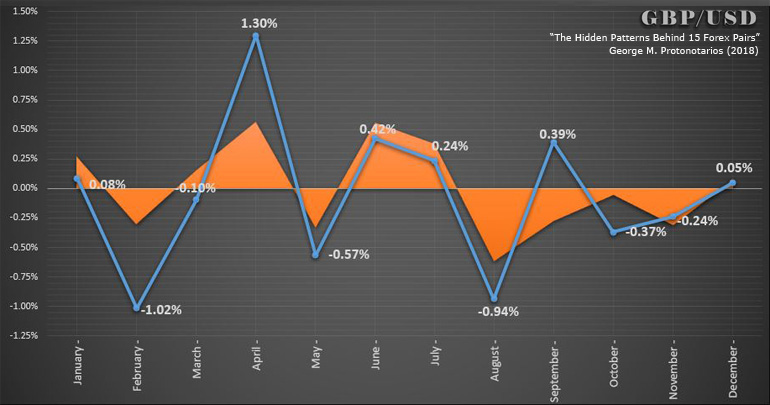
The GBP statistics above, along with data on 15 major Forex pairs, are featured in the book: “The Hidden Patterns Behind 15 Forex Pairs – Revealing Momentum and Seasonal Patterns Based on 18.5 Years of Daily Exchange Rates.”
You can purchase it from the following marketplaces:
► The book ‘Hidden Patterns’ at Payhip (.PDF)
Investing in the Interest Rate Differential (Carry Trade Strategy)
The carry trade is a popular Forex strategy that leverages interest rate differences between two currencies. The core idea is simple:
-
Buy (go long) a high-yielding currency (with a higher interest rate).
-
Sell (go short) a low-yielding currency (with a lower or near-zero interest rate).
The objective is to earn the interest rate differential—known as the “carry”—while also potentially profiting from favorable exchange rate movements.
How the Carry Trade Works
Interest Rate Arbitrage
Traders borrow funds in a low-interest-rate currency (e.g., Japanese Yen, Swiss Franc) and invest in a high-interest-rate currency (e.g., Australian Dollar, New Zealand Dollar).
Profit comes from the daily interest differential paid by the broker (often called the swap or rollover).
Exchange Rate Stability Matters
-
If the high-yielding currency appreciates, traders benefit from both interest income and capital gains.
-
If the high-yielding currency depreciates, exchange losses may offset or exceed the interest earned.
Long-Term Holding Period
Carry trades are typically held for extended periods—weeks, months, or even years—unlike short-term day trades.
The longer the position remains open, the more swap income is accumulated.
Table: Popular Currency Pairs for Carry Trades
|
Currency Pair |
Why It’s Used in Carry-Trade |
|---|---|
|
Australia’s higher rates vs. Japan’s near-zero rates |
|
New Zealand’s attractive yields vs. JPY’s low rates |
|
Turkey’s high interest rates (but with high risk) |
|
UK’s moderate rates vs. Switzerland’s negative rates |
Why Brokers Pay the Interest Rate Differential
Forex brokers adjust open positions daily. The interest rate differential between the two currencies is either credited or debited to the trader’s account.
High-yield currencies tend to lose value over time due to inflation, and the interest payments help compensate for that risk.
Pros & Cons of Carry Trading
✅ Pros:
✔ Steady passive income through swap payments
✔ Effective in low-volatility, trending markets
✔ Aligned with central bank tightening cycles (e.g., rising rates)
❌ Cons:
✖ Exchange rate risk—losses can exceed interest gains if the high-yielding currency drops
✖ Liquidity risk—emerging market currencies (e.g., TRY, ZAR) can experience sudden price gaps
✖ Requires patience—not suitable for short-term trading
Final Thoughts
The carry trade can be a profitable long-term strategy, offering passive income through interest rate differentials. However, success depends on:
-
Careful currency pair selection (avoid highly volatile pairs)
-
Solid risk management (e.g., hedging and stop-loss strategies)
-
Monitoring macroeconomic indicators (such as central bank decisions and inflation data)
For traders seeking passive income and exposure to global monetary trends, the carry trade provides a compelling opportunity—though not without its risks.
More on Carry-Trade Strategy: ► Carry-Trade Strategy
■ The Basics of Investing in the Foreign Exchange Market
Forex-Investors.com (c)
□ More on Forex: » Getting Started | » Forex Investing | » Exchange Rates History | » Forex Risks | » Forex Regulation □ Find More: » Brokers Directory | » Automated Trading Systems










