Risk Management in Foreign Exchange Investing
 Like all financial markets, the Foreign Exchange market carries various risks. Therefore, effective risk management is essential for achieving long-term profitability. This analysis outlines the major currency risks and provides specific recommendations for managing them.
Like all financial markets, the Foreign Exchange market carries various risks. Therefore, effective risk management is essential for achieving long-term profitability. This analysis outlines the major currency risks and provides specific recommendations for managing them.
Six Major Risks
There are six (6) key risks associated with investing in the Foreign Exchange market:
(1) Exchange Rate Risk
Exchange rate risk is a form of market risk that arises from unfavorable fluctuations in exchange rates. Every active Forex position is exposed to this risk. While it cannot be completely eliminated, its impact can be significantly reduced.
Hedging Against Exchange Rate Risk:
Here are some basic strategies to hedge against currency risk:
-
Diversifying your investment portfolio
-
Implementing a comprehensive Money Management (MM) system
-
Trading with smaller position sizes
-
Minimizing the use of leverage
-
Identifying and managing potential correlations between different currency positions
(2) Correlation Risk
Certain Forex pairs exhibit strong correlations. Correlation risk refers to changes in the relationship between two financial instruments over time. This risk can undermine the effectiveness of portfolio diversification, making it an important consideration for Forex investors.
For example, the historical correlation between NZD/USD and EUR/USD has declined over the past decades. In contrast, the correlation between GBP/USD and EUR/USD has increased.
Table: Historical Correlations Between Major Forex Pairs
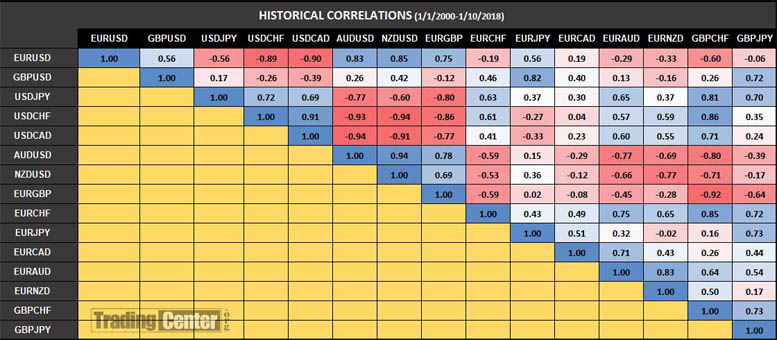
The table above presents the correlations among fifteen (15) major Forex pairs for the period 2000–2018. It is sourced from the book Historical Correlations Between Major Forex Pairs.
► more about the book on Amazon
Hedging Against Correlation Risk
1. Diversification with Non-Correlated Pairs
-
Instead of trading multiple positively correlated pairs (e.g., EUR/USD and GBP/USD), balance exposure with uncorrelated or negatively correlated currencies (e.g., USD/JPY or USD/CAD).
2. Using Options for Dynamic Protection
-
Buying Forex options (such as puts or calls) allows traders to limit downside risk while maintaining upside potential.
3. Cross-Hedging with Correlated Assets
-
Since Forex pairs are influenced by commodities, bonds, and equities, traders can hedge using related instruments.
4. Rolling Hedges with Futures Contracts
-
Forex futures (such as CME contracts) allow traders to lock in exchange rates for future dates, reducing uncertainty.
-
If a trader expects correlation breakdowns due to an upcoming event (like an FOMC meeting), they can adjust futures positions accordingly.
5. Monitoring Correlation Coefficients in Real-Time
-
Traders should regularly check correlation matrices (available on platforms like MetaTrader, TradingView, or Bloomberg) to detect weakening relationships.
-
If historically strong correlations (e.g., EUR/USD and GBP/USD at +0.8) drop below +0.5, it may signal a need to adjust hedges.
(3) Interest Rate Risk
Interest rates are central to the valuation of exchange rates. A decision to change interest rates can significantly impact currency markets, especially if the decision is unexpected.
Here’s how interest rate risk can affect a portfolio:
(i) Sudden exchange rate volatility
(ii) Stop-loss triggers and forced position closures
(iii) Reversals in long-term Forex trends
(iv) Changes in overnight rates (SWAPs), which significantly affect carry traders
Hedging Against Interest Rate Risk
- Trading small position sizes allows for wider stop-loss orders, reducing vulnerability to volatile events such as interest rate announcements.
- In the short term, traders should avoid market exposure during scheduled interest rate decisions.
3- Credit Risk
In Forex trading, credit risk can take several forms. Most commonly, it refers to the risk that a Forex broker may fail to meet its financial obligations to clients, especially in the event of bankruptcy.
Hedging Against Credit Risk
(i) Trade with regulated brokers that offer fully segregated client bank accounts
(ii) Understand the investor compensation scheme and regulatory framework of the broker’s country
(iii) Maintain multiple trading accounts across different brokers, rather than concentrating funds in a single large account
4- Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk is the inability to liquidate an investment and access cash when needed. A lack of liquidity can disrupt payment agreements, making this risk particularly significant. In other words, an investment should not only be safe but also easily liquidated.
While the Forex market is the most liquid market in the world, liquidity risk still exists. Notably, in 2015, the Swiss franc surged 30% after the Swiss National Bank removed its currency cap against the Euro, causing major brokerage firms such as Alpari UK to go bankrupt.
Hedging Against Liquidity Risk
(i) Trade small positions (note: stop-loss orders may not trigger in extreme cases)
(ii) Know the compensation scheme and the regulatory jurisdiction of your broker
(iii) Distribute funds across multiple brokers rather than relying on a single account
5- Political Risk or Country Risk
Political or country risk involves unexpected legislative changes that may negatively impact currency values. Events like capital controls can trigger extreme volatility. Emerging and developing markets tend to carry higher political risks than developed ones.
Hedging Against Political Risk
(i) Political risk is best managed through broad portfolio diversification.
6- Systemic Risk
Systemic risk refers to the potential collapse of the entire financial system. As markets become increasingly globalized, a crisis in one market can quickly spread, triggering a worldwide collapse. Though rare, systemic crises can result in a complete loss of capital.
Hedging Against Systemic Risk
(i) Hold physical gold and Bitcoin as part of your portfolio
(ii) Diversify your portfolio across multiple asset classes and regions
Key Takeaways & Tips
Opening a position in any financial market—whether in stocks, Forex, commodities, or derivatives—exposes you to a wide range of risks, including market volatility, liquidity constraints, geopolitical events, and unexpected economic shifts. These risks can lead to significant losses if not properly managed. Price fluctuations, sudden news events, and leverage-related wipeouts are just a few examples of the dangers traders and investors face daily. Consistently hedging against these risks is not just a best practice—it’s a necessity for survival in the markets. Hedging involves using strategies such as options and futures to offset potential losses in a primary position.
Effective risk management is the defining factor of long-term success for any investor, separating the professionals from the reckless gamblers. This includes setting stop-loss orders, diversifying portfolios, sizing positions appropriately, and never risking more than a small percentage of capital on a single trade. The most successful investors and fund managers prioritize capital preservation over aggressive speculation, knowing that consistent, disciplined strategies outperform short-term luck.
Professional investors always hedge their positions and avoid trading “naked” (taking unhedged, directional bets) because they understand that no trade is ever guaranteed. Even the most confident market thesis can be wrong, and without protection, a single bad trade can wipe out weeks or months of gains. By maintaining hedges, professionals ensure they can weather adverse conditions and remain profitable over time, rather than falling victim to unpredictable market swings.
Below are key strategies for managing all forms of risk:
Six (6) Key Tips for Managing Forex Investment Risk
(i) Multi-level portfolio diversification — No exceptions
(ii) Brokerage diversification — Maintain accounts with multiple brokerage firms
(iii) Trading account diversification — Deposit funds only within limits covered by compensation schemes
(iv) Trade small position sizes — A professional trader risks no more than 2% of portfolio value on any single trade
(v) Avoid high trading leverage — Leverage increases both risk and trading costs
(vi) Prepare for black-swan events — Allocate part of your portfolio to physical gold
■ Foreign Exchange Risks & Risk Management
George Protonotarios, January 2020
Forex-investors.com (c)
□ More on Forex: » Getting Started | » Forex Investing | » Exchange Rates History | » Forex Risks | » Forex Regulation □ Find More: » Brokers Directory | » Automated Trading Systems









